Project Report - Consul Key-Value Store!
January 05, 2020
Title: Consul Key-Value Store
Project Description:
The project aims to provide a REST/CLI solution to access a key-value store. More precisely, it provide a Get and Set interface for getting keys and storing data/values respectively.
Installation / Usage Instructions:
Tools/softwares/services used:
Pre-requisites:
- A VM/server for hosting the Consul web UI.
Note: I am using GCP Compute-Engine VM instances for my solution.
Steps:
-
Create a GCP compute-engine VM instance (in my case, an Ubuntu 18.04 LTS VM, n1-standard-1, 1 vCPU, 3.75 GB memory). Refer this article for the steps to create and connect to a Google Cloud VM via SSH.
- Once you SSH into the VM, the next step is to setup Consul (which is an open-source service networking solution to connect and secure services across any runtime platform and public or private cloud). The official documentation provides two ways to install Consul:
- Using a precompiled binary
- Installing from source
- I will be using the first option for my setup. Here, we are required to download the latest appropriate package for our system (which basically is a zip file of pre-compiled binaries. It might require to install
unzippackage in case it is not already available (command:sudo apt install unzip)).
$ wget "https://releases.hashicorp.com/consul/1.6.2/consul_1.6.2_linux_amd64.zip"
$ unzip consul_1.6.2_linux_amd64.zip
- As it is a precompiled binary, the only requirement to have it running is to put the unzipped file in one of our system path setup in our machine.
$ echo $PATH
# I will be adding it to the directory path `/usr/local/sbin`.
# You can add it to any of the path specified in the above output.
$ sudo mv consul /usr/local/sbin
- And that is all about the Consul setup/installation. You can verify the installation by running the command
consuland the output will look like the following.
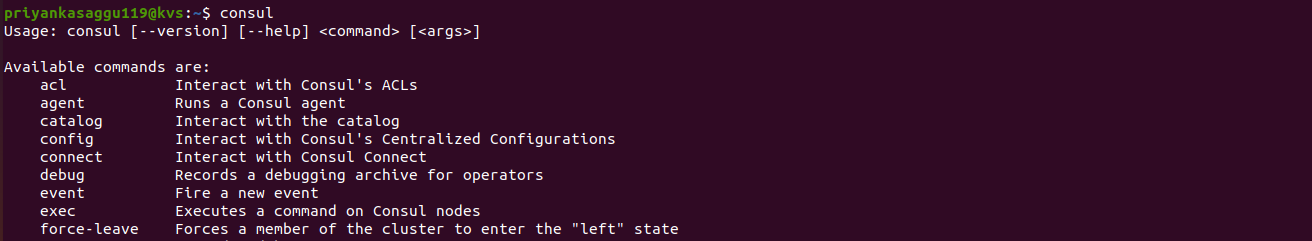
Workflow
The workflow for the solution is quite easy and straight-forward. We basically need to do the following:
-
Create a Consul config-file in directory
./consul.dfor ensuruing a smooth access of the Consol web UI.$ mkdir ./consul.d $ echo '{ "client_addr":"0.0.0.0" }' > ./consul.d/web.json -
Run the Consul Agent, passing the above config-file in the
-config-dirflag. (Make sure that it keeps running inside one terminal session throughout the rest of the process)$ consul agent -dev -enable-script-checks -config-dir=./consul.d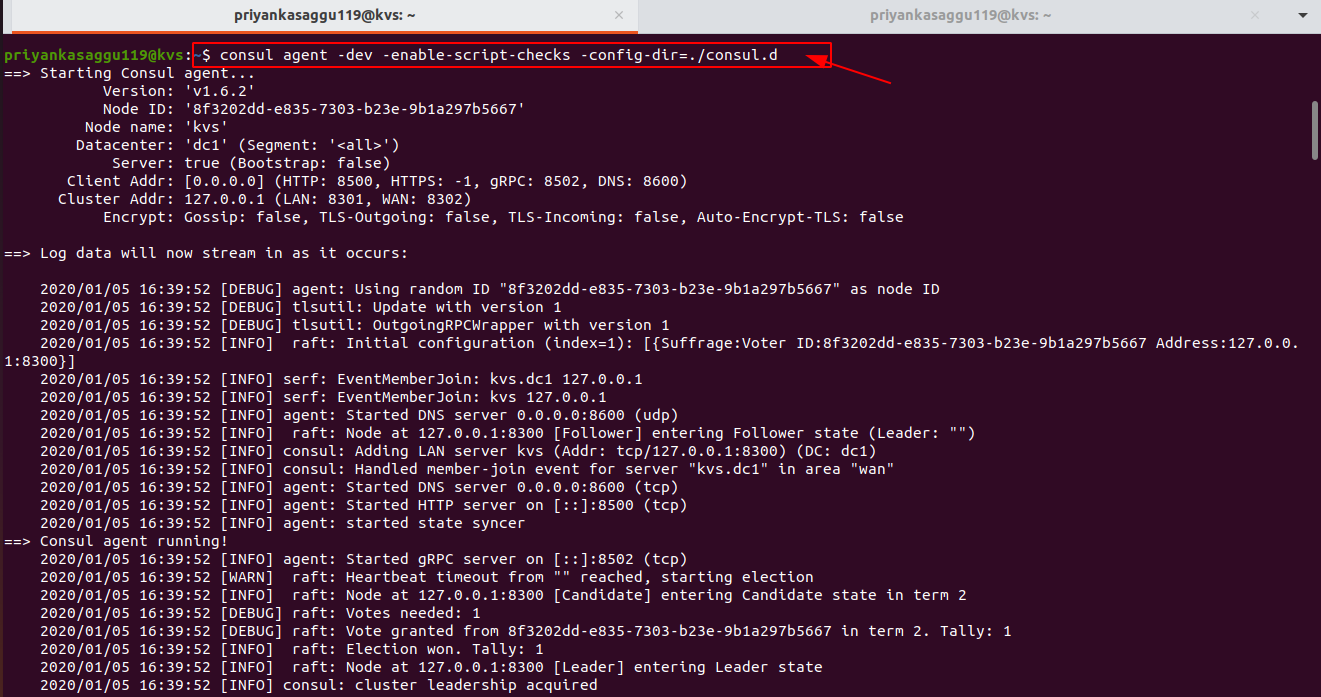
-
Inside a new terminal session, use the
Consul kvcommand line interface (CLI) to create a new key/value store. We’ll use this Consul Key/Value store to add and retrieve key-value pairs.- Below are some of the example commands to demonstrate the process of storing (put) keys and retrieving (get) values from the Consul kv store.
# set up a key:value pair <foo:bar> and retrieve the value for key 'foo'. $ consul kv put foo bar $ consul kv get foo # set up another key:value pair <hello:priyankasaggu119> and retrieve the valur for key 'hello'. $ consul kv put hello priyankasaggu119 $ consul kv get hello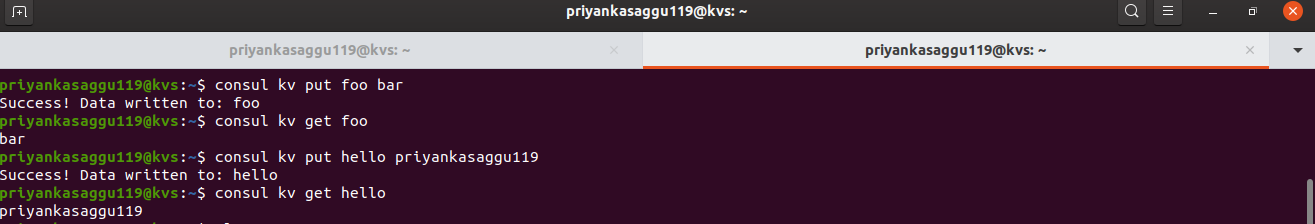
- To check some additional metadata about the key-value pairs, use the
-detailedcommand line flag.
$ consul kv get -detailed hello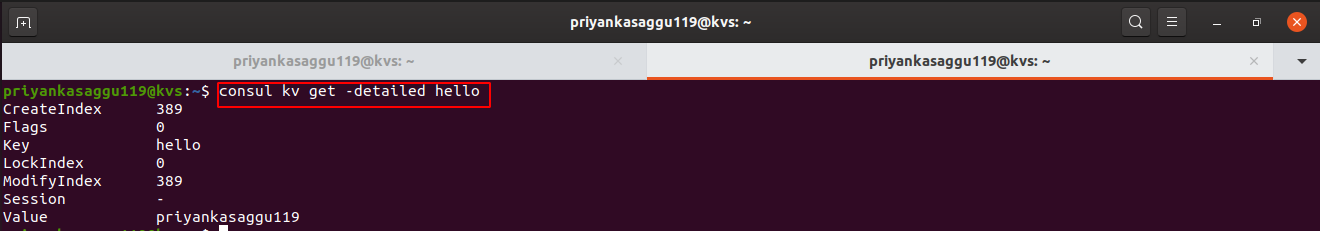
- To list all the key-value pairs in a lexicographical order, use the
-recursecommand line flag.
$ consul kv get -recurse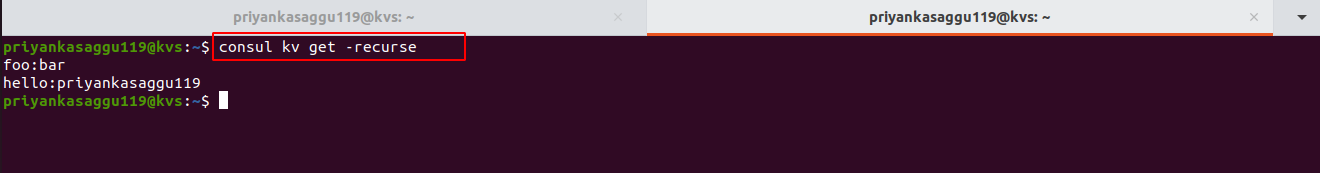
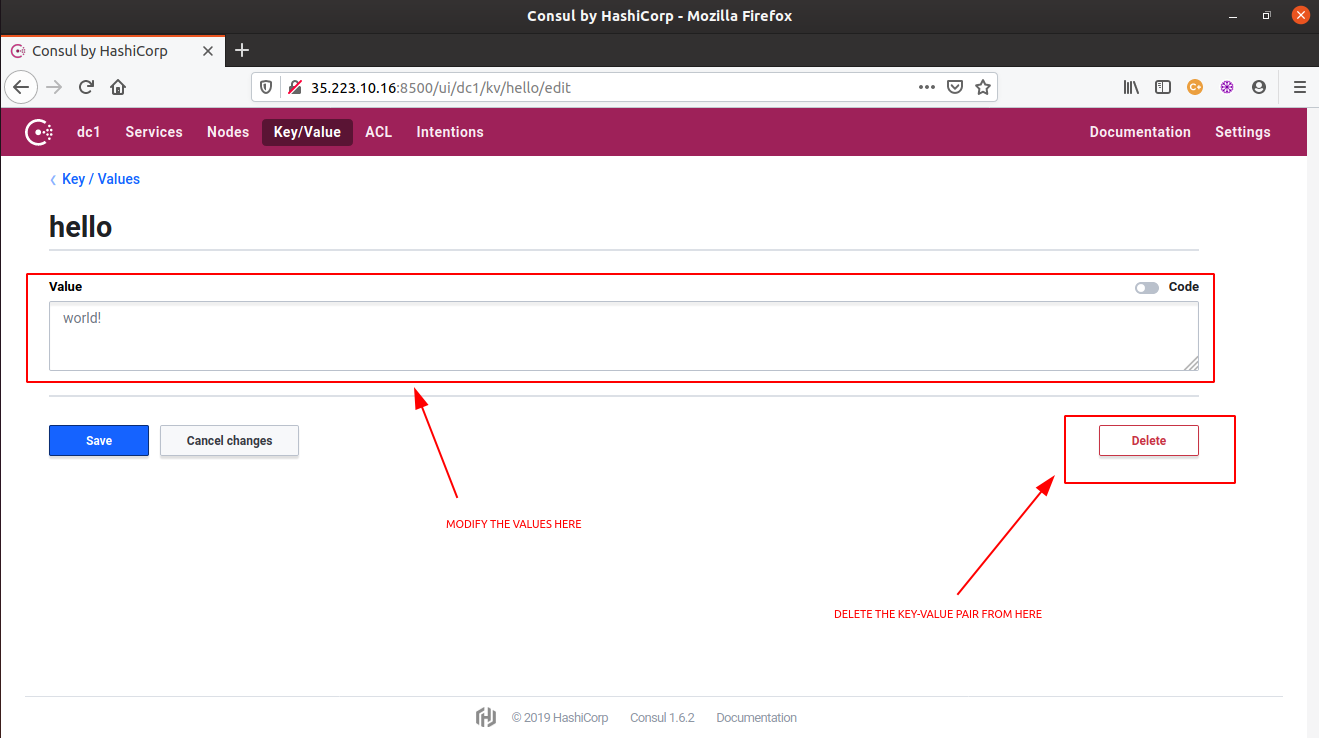
- To modify the value for an existing key, issue the same
consul kv getcommand for a key with a new value.
# Let's try to modify the value for the key "hello". $ consul kv put hello world!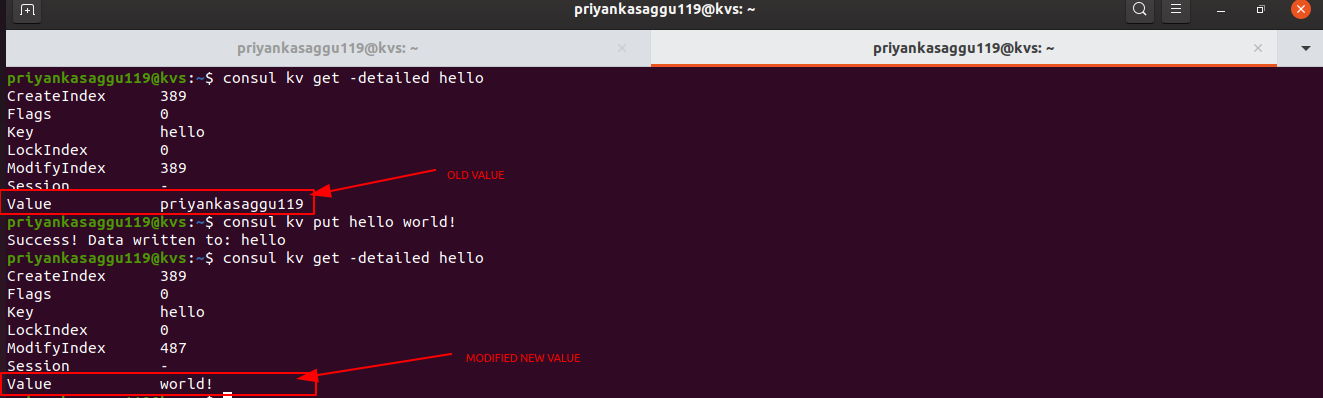
- And finally, to delete a key-value pair from the Consul kv store, use the
deletecommand.
# adding an extra key:value pair <One:1> for demo. $ consul kv put One 1 $ consul kv delete One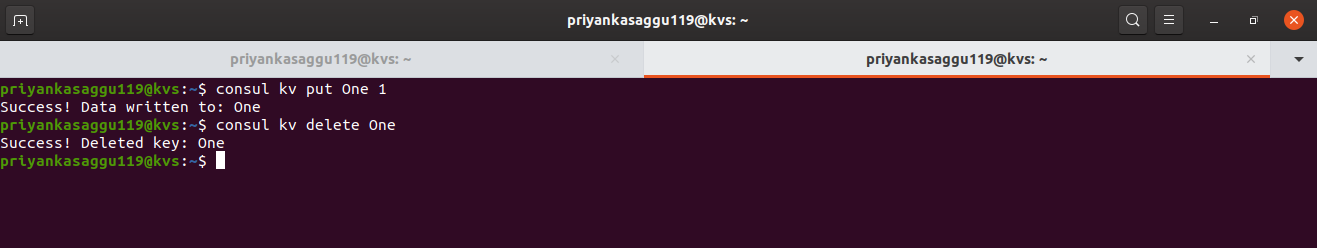
-
With Consul web UI, One can perform all the above operations in a more efficient and easier way.
- To launch the Consul web UI, access the url,
http://<vm-ipaddress>:8500/uiin a browser window. (Note: It requires to add a separate firewall rule for exposing port 8500 of the GCP VM. Use this guide for instructions.)
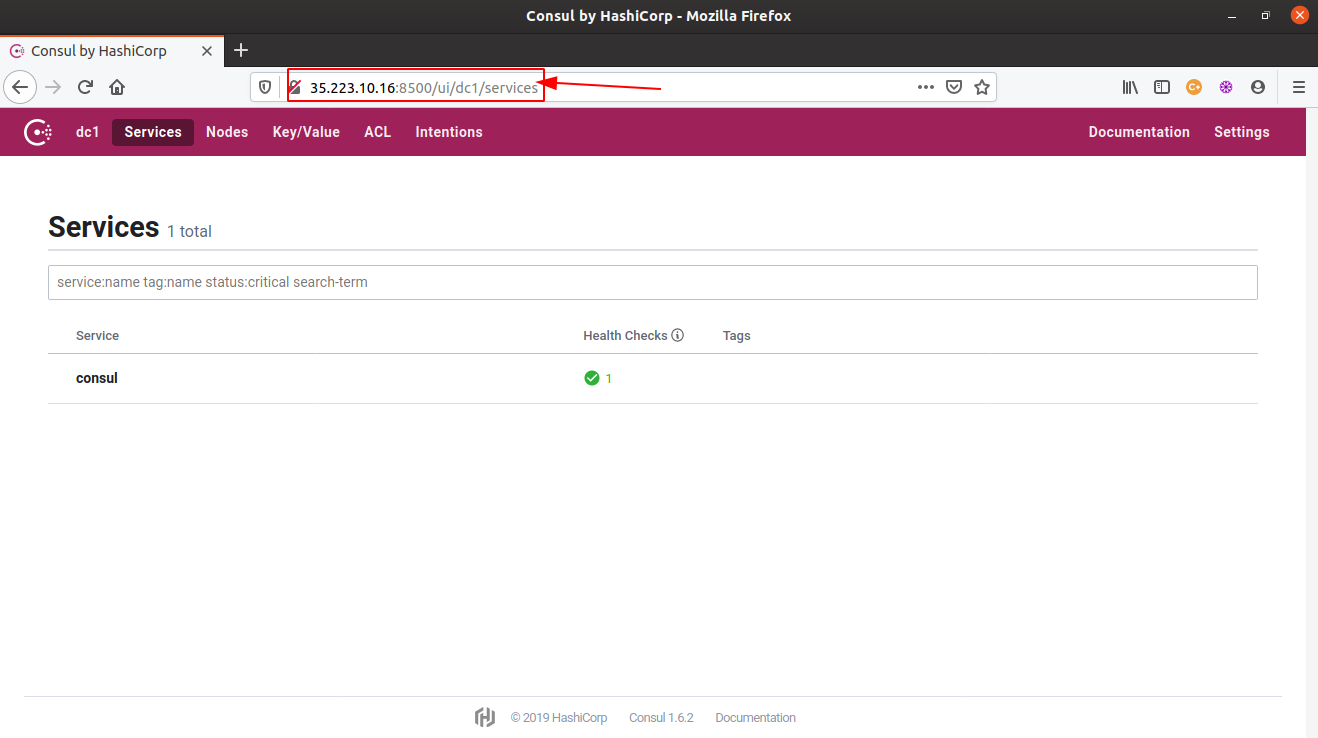
- Head onto the
Key/Valuesection in the navigation bar and you will see all the key-value pairs listed there.
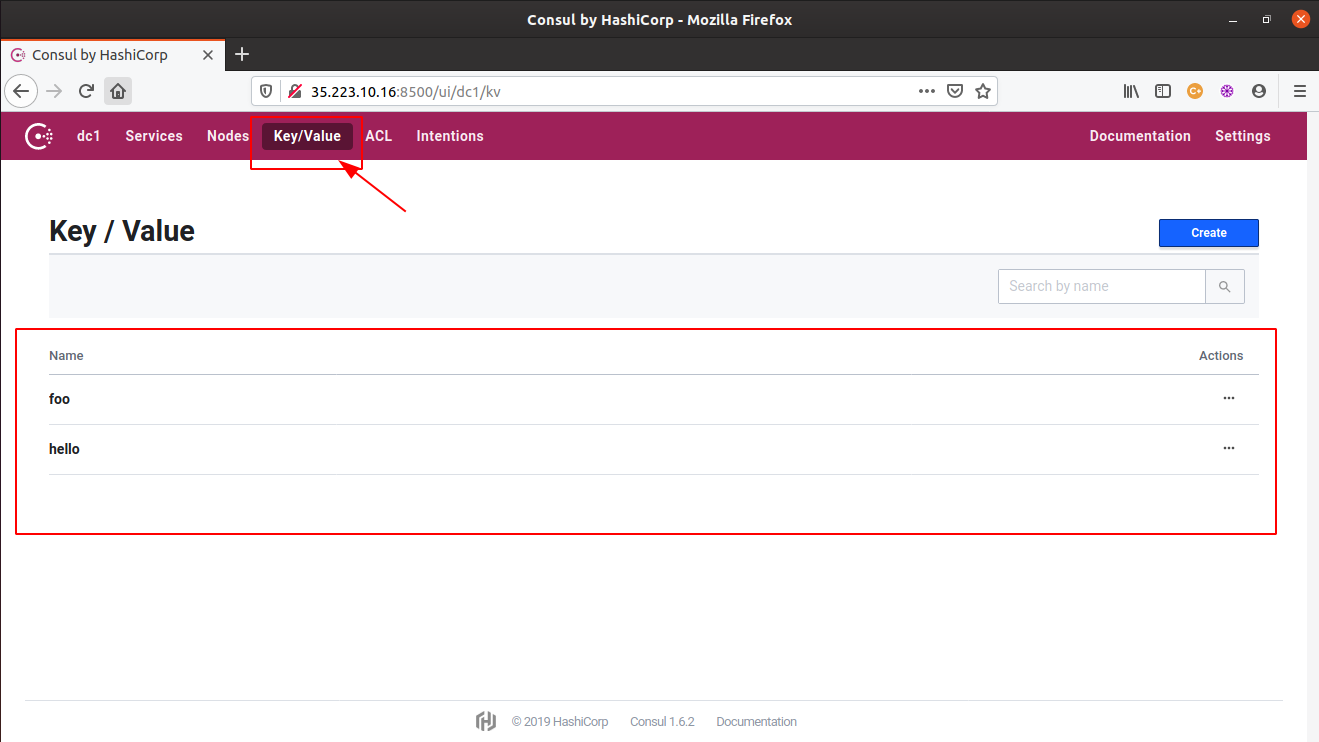
- All the above Consul CLI operations can be more easily performed using the Consul web UI. From creating a new key-value pair to modifying the existing values, or even deleting the existing key-value pairs, everything can be done from this single UI itself.
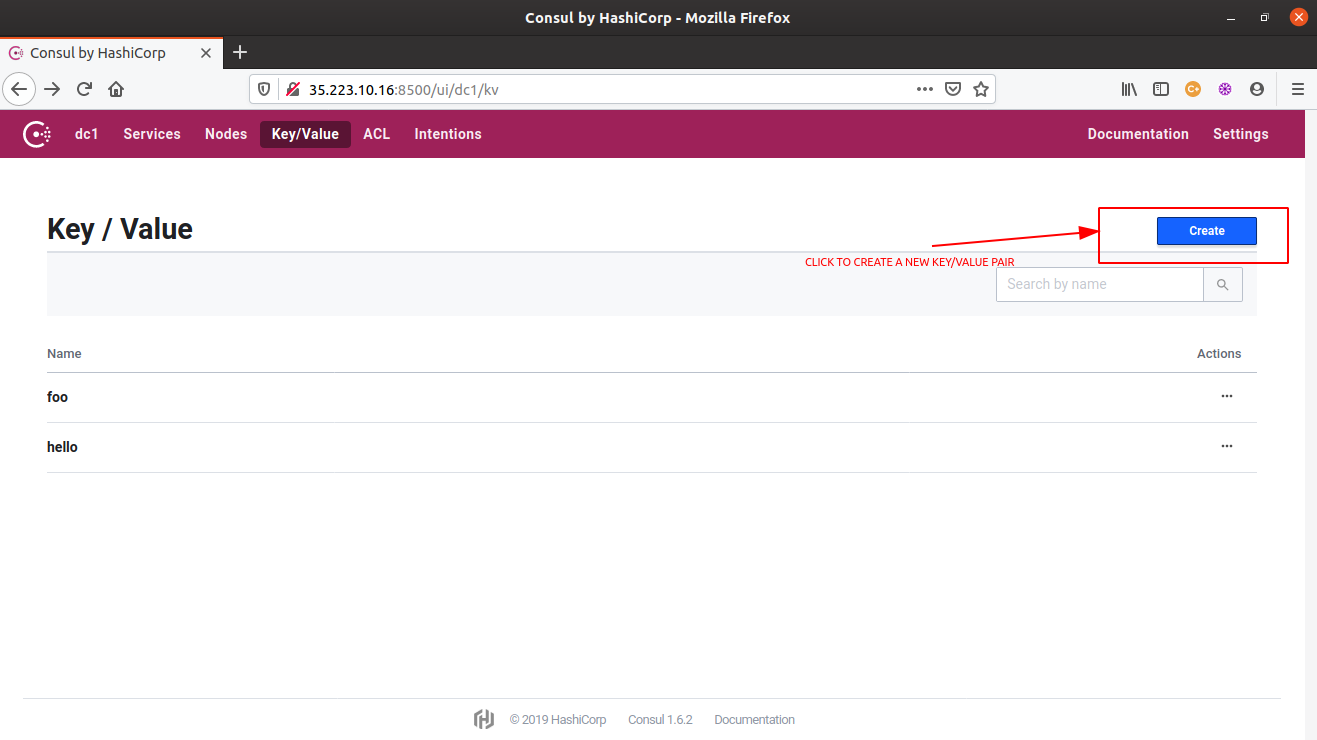
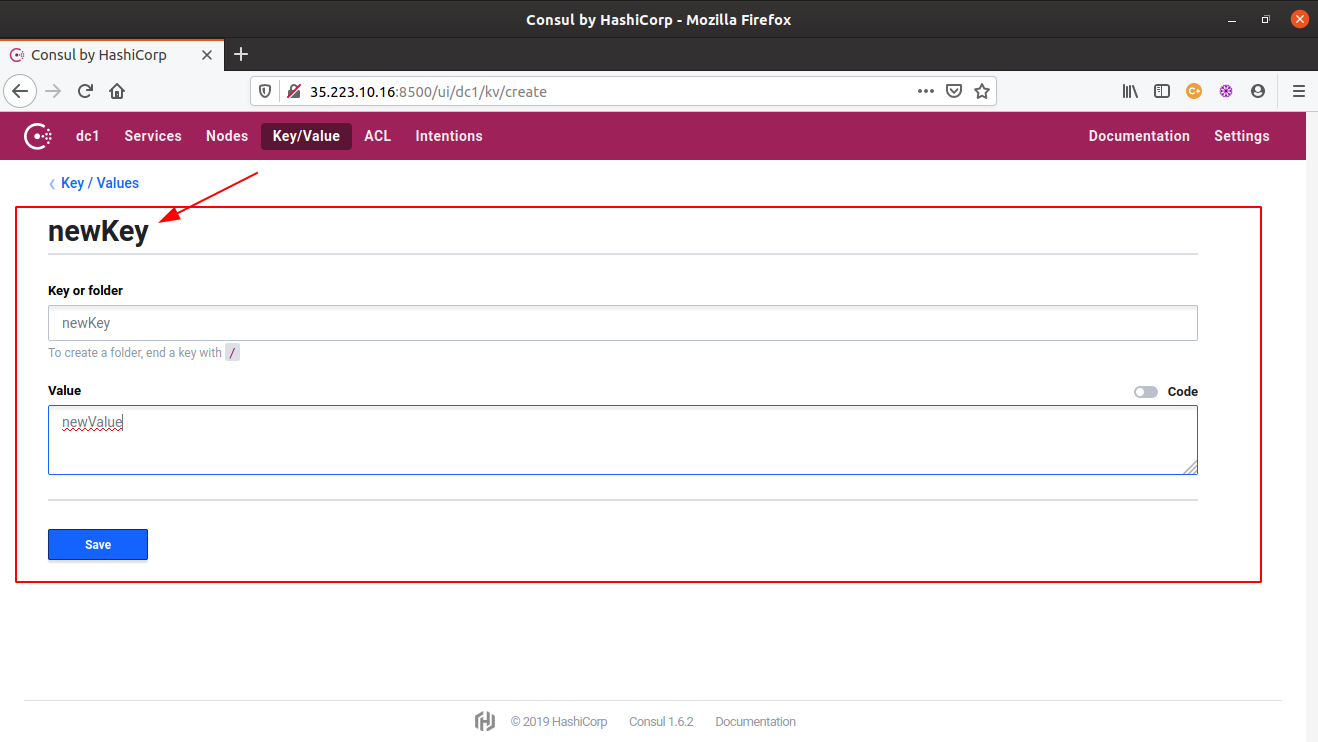
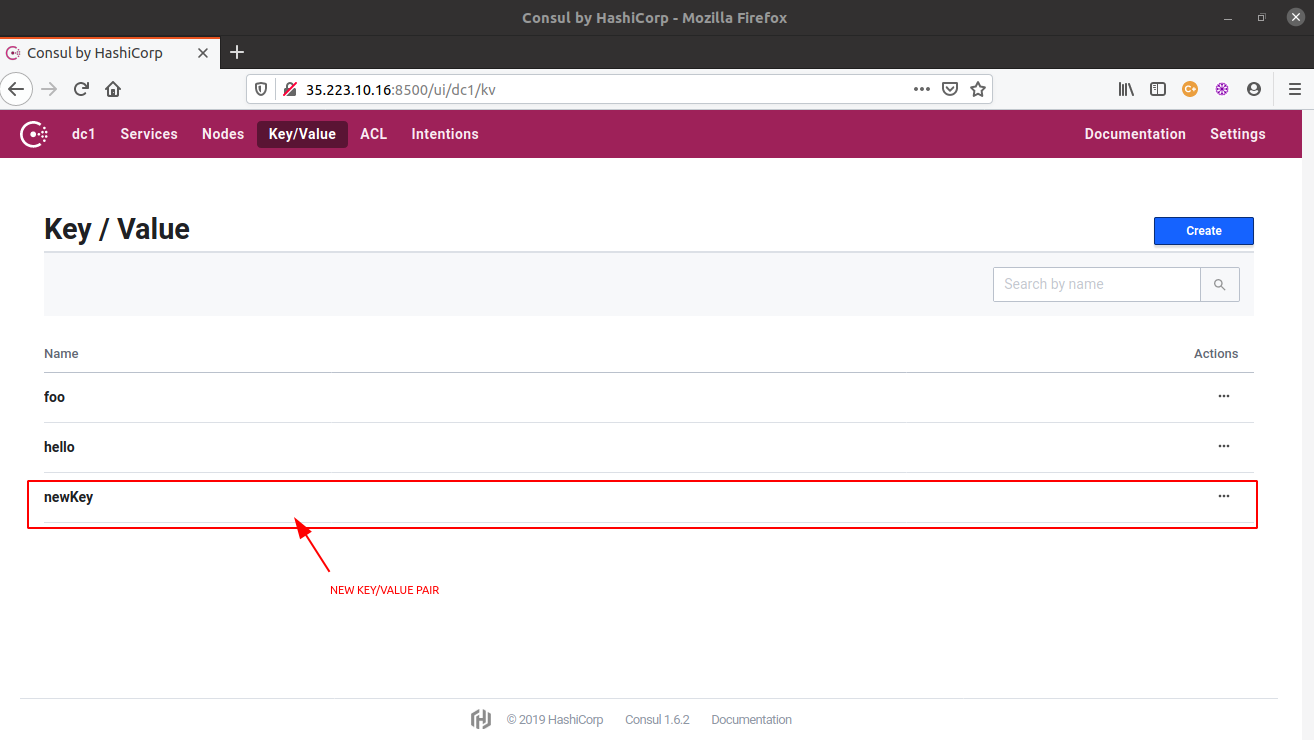
- To launch the Consul web UI, access the url,
-
Apart from the local command line Interface (CLI) and the Consul hosted web UI, it is possible to query the Consul key/value store from a remote machine as well using
curlcommand.# For example, to get the value and other metadata for key "hello". $ curl http://35.223.10.16:8500/v1/kv/hello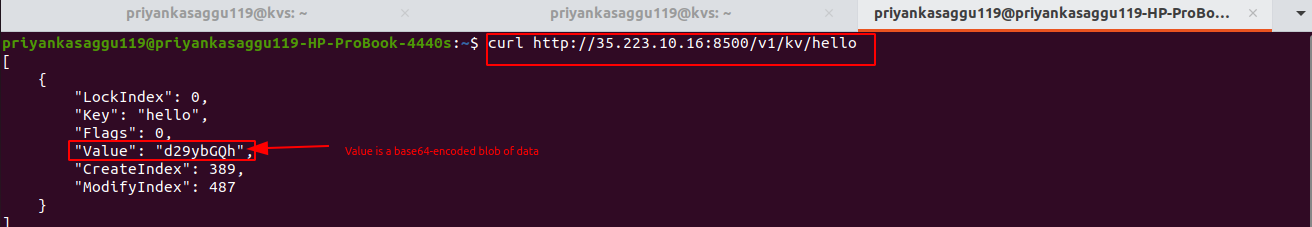
- To add a new key/value pairs from the remote machine,
curlcommand will be used with aPUTrequest flag.
# we are trying to add a new key:value pair <name:priyanka> here. $ curl --request PUT --data "priyanka" http://35.223.10.16:8500/v1/kv/name true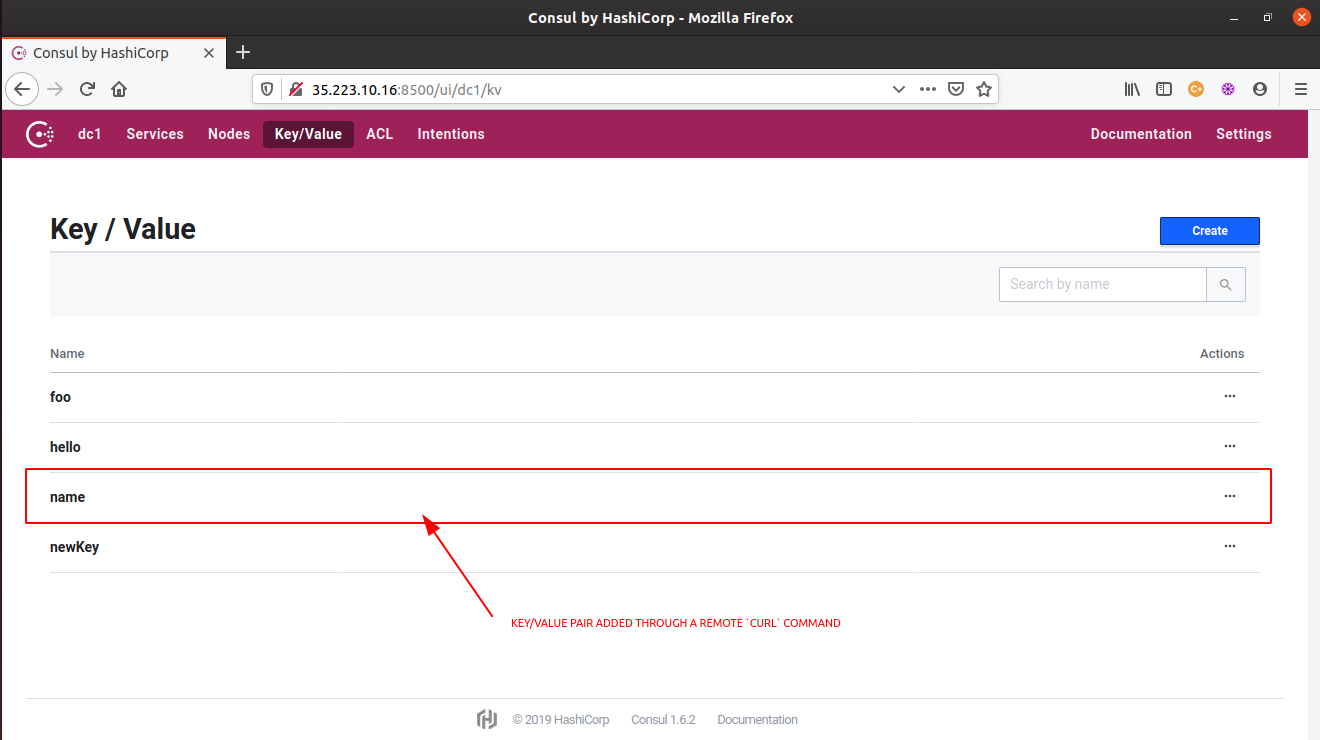
- Similarly, a key/value pair can be deleted using a
curlcommand withDELETErequest flag.
# we are trying to delete the key:value pair with key "name". $ curl --request DELETE http://35.223.10.16:8500/v1/kv/name true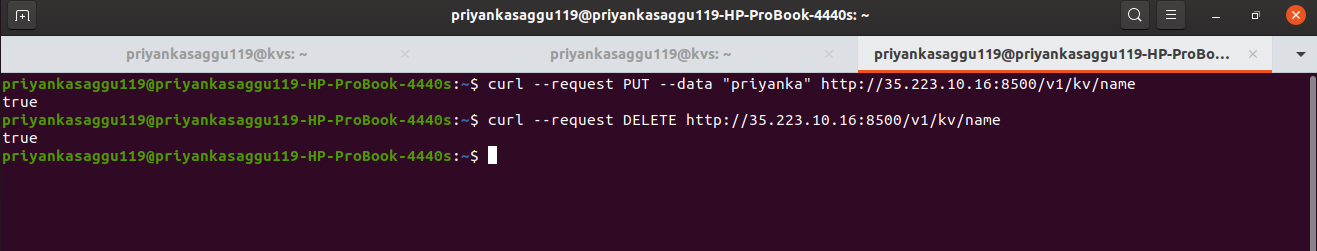
- To add a new key/value pairs from the remote machine,
Use Cases, Edge Conditions and Assumptions
The above solution assumes the current setup to be a development environment. Ideally it requires a multi-server Consul setup to achieve a production level, secure environment, which is currently less probable to achieve with the limited amount of computing resources I have.